In the early days of Ultimate, our testing tool was a paid AI solution used to manage suites, quickly anchor automated tests and enable schedule and on-demand executions. As we grew, we knew this was not the tool to meet our demands and also we were not deriving the expected value from this solution. Each features such as adding more browsers comes at an extra cost.
Likewise, in the face of a relentless tide of new features and enhancements, our lean quality engineering team found it increasingly challenging to keep pace and anchor tests accordingly. It became evident that we needed a tool that not only appeals to developers but also fostered a shared responsibility for product quality.
Other known challenges includes:
Execution Time: As our application expands so do the number of test cases, leading to longer execution times. In most cases, it takes an average of 25 mins for execution of our full suites.
Resource Utilization: Having concurrent execution put a strain on resources and causes test executions to hang or terminate especially with browser automation
Flakiness: This was a common issue faced by the team. Managing and troubleshooting flaky tests are always time consuming
Lets distribute the tests: Sharding
Sharding in Playwright is a concept that allows test distribution across multiple instances, thereby optimizing resource utilization and reducing overall execution time.
Playwright supports parallel execution of test files. To further scale our test execution, we execute these test files across multiple machines, called shards, thereby ensuring efficient utilization of resources while adapting to variations in test load.
In addition, by isolating test execution within individual shards, we enhance test stability and reliability. Failure in one of the shards will have no impact on the other.
CI setup
Delving into how we use Playwright shard in Ultimate. We create feature-based suites, which are small subset of tests related to the same features, as test files.
In Github Actions, we use jobs for sharding tests. The workflow runs the tests on self-hosted runners, qe-runners, the shards, having chromium browsers pre-installed (to speed up the test). Also, we use a matrix strategy for executing the tests in parallel across the different shards. In this case, it’s set up to run the tests on the chromium project, with 5 different shards (shardIndex: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).
jobs:
test:
runs-on: qe-runners
permissions:
contents: "read"
id-token: "write"
strategy:
fail-fast: false
matrix:
project: [chromium]
shardIndex: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
shardTotal: [5]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version-file: '.nvmrc'
- name: Install playwright
run: npm ci
- name: Check version
run: npx playwright --version
- name: Run tests
run: |
npx playwright test --project=$ --shard=$/$
env:
USER_PWD: $
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: $
- name: Upload blob (shard) reports to GitHub Actions Artifacts
if: always()
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: all-blob-reports
path: blob-report
retention-days: 1
Next, each of these shards generate its reports, so for ease of use we merge the reports. We get the merged (zipped) file from Github and upload to our Google Cloud Storage to free up Github resources. Also we send test summary as slack notification.
Note: we only retain the artifact in github for a day for cost effectiveness, and we upload the artifacts in the Google Cloud bucket for a longer period.
merge-reports:
if: always()
needs: test
runs-on: qe-runners
permissions:
contents: "read"
id-token: "write"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version-file: '.nvmrc'
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Download blob reports from GitHub Actions Artifacts
uses: actions/download-artifact@v3
with:
name: all-blob-reports
path: all-blob-reports
- name: Merge into HTML and JSON Report
run: PLAYWRIGHT_JSON_OUTPUT_NAME=results.json npx playwright merge-reports --reporter=html,json ./all-blob-reports
- name: 'Google Auth'
if: always()
id: 'auth'
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v1'
with:
token_format: "access_token"
workload_identity_provider: '$'
service_account: '$'
project_id: '$'
- name: 'Set up Cloud SDK'
if: always()
uses: 'google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v1'
with:
project_id: '$'
install_components: 'alpha'
- name: Get current date
run: |
currentDate=$(date '+%Y%m%d')
echo "CURRENT_DATE=$(date '+%Y%m%d')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Upload test results
uses: 'google-github-actions/upload-cloud-storage@v2'
with:
gzip: false
path: playwright-report/
destination: $/$/$/scheduled/
if: always()
id: upload_to_bucket
- name: Post test run summary to slack
env:
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: $
REPORT_LINK: "https://report.XXXXXXXX/$/$/playwright-report/index.html"
TYPE: 'scheduled'
STARTED_BY: $
run: |
npx playwright-slack-report --config="${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/cli_config.json" --json-results="${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/results.json"
Notification:
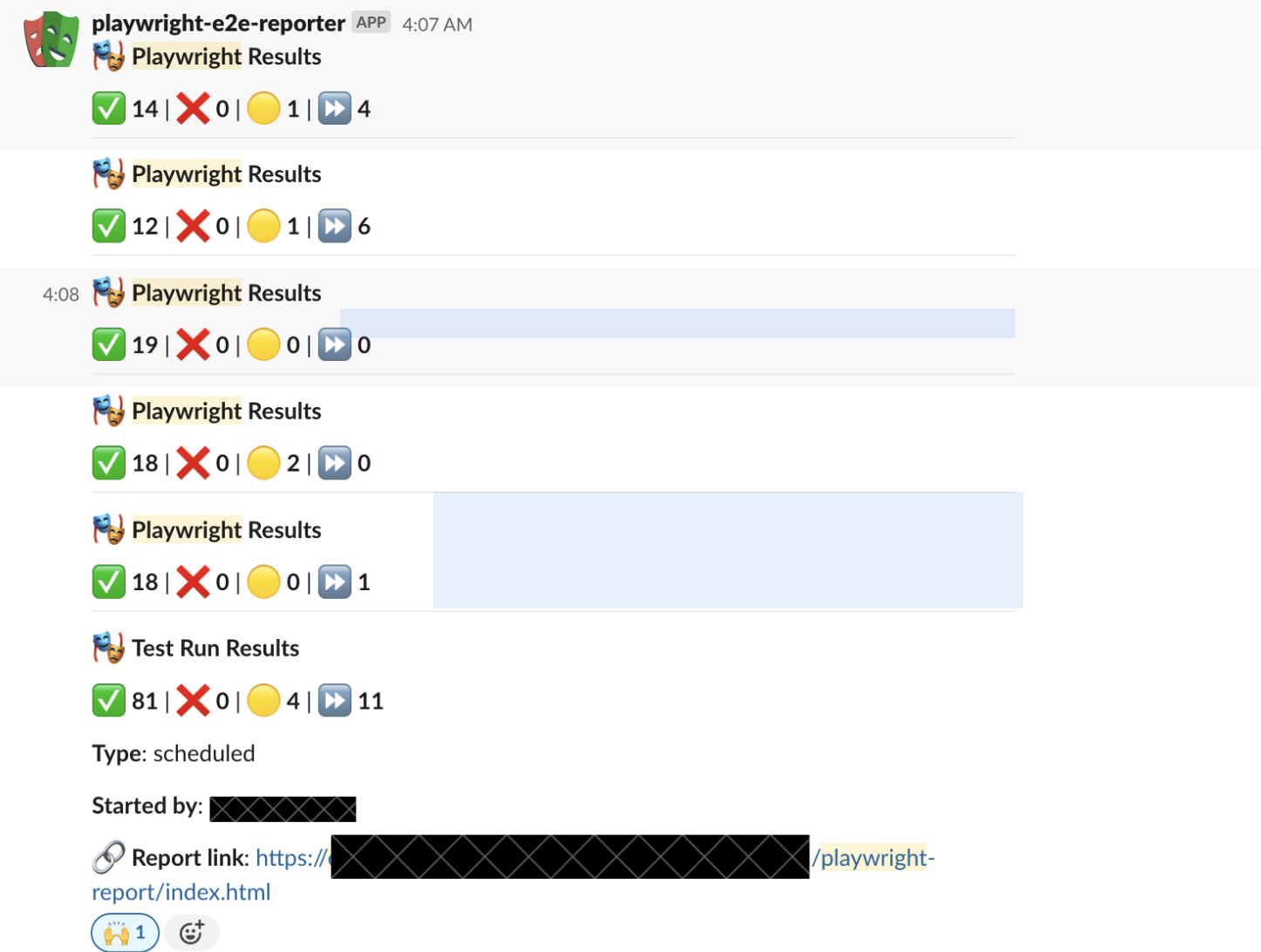
Finally, we provide the link to the Artifact in Google Cloud, this announce job runs after the merge-reports job.
announce:
runs-on: qe-runners
needs: merge-reports
if: always()
permissions:
contents: "read"
id-token: "write"
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Announce in job
if: always()
run: |
currentDate=$(date '+%Y%m%d')
echo "Your artifact is in [this gcp bucket](https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser/$/$/$currentDate/) " >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
Artifacts:
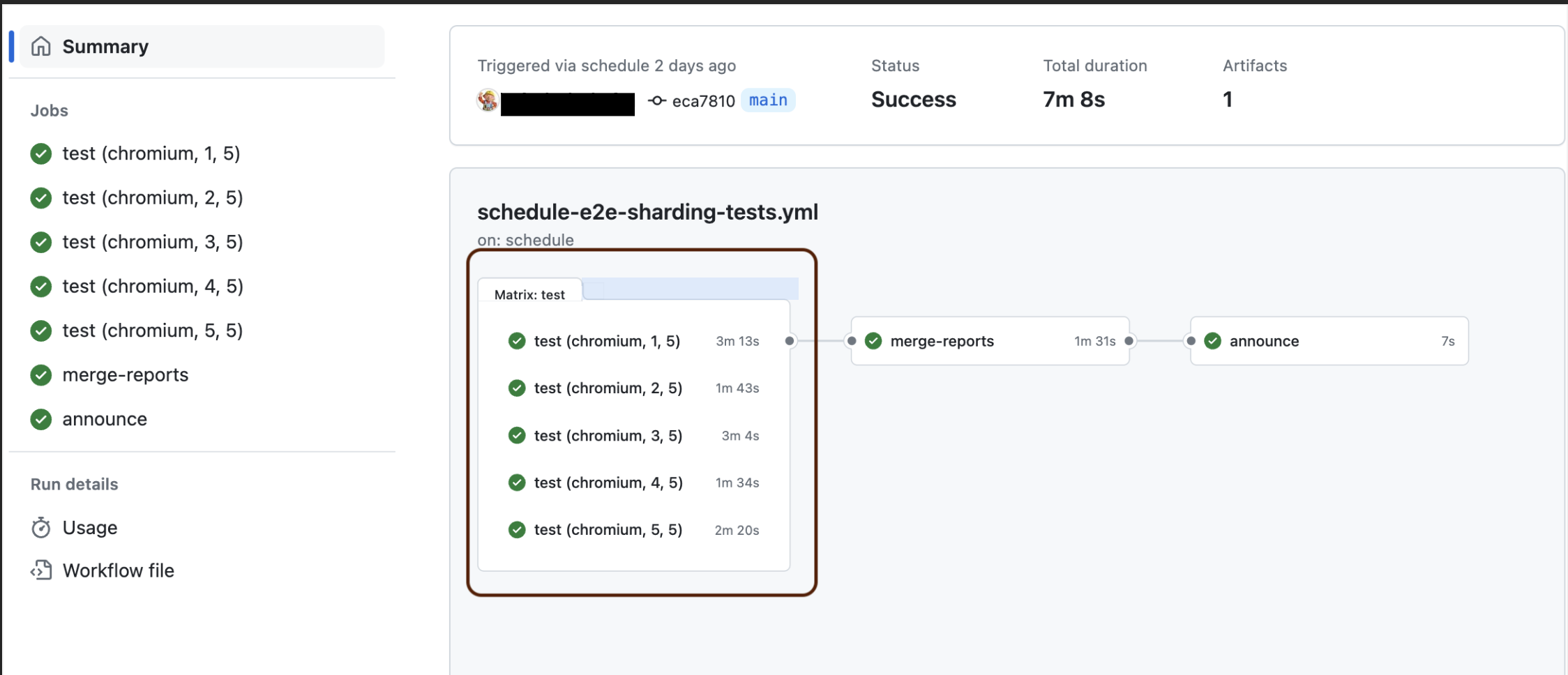
As we can see, with sharding the maximum execution time for the tests was just over 3 mins, while the overall duration for the whole job is approximately 7 mins rather than 25 mins with previous automation tool.
Jobs Summary:
To help promote the shift left approach, we have included the workflow to trigger on every PR raised. This allows the developers to run comprehensive tests early and often, thereby identifying and resolving issues promptly.
Conclusion
Playwright sharding represents a significant advancement in the field of E2E testing, offering a scalable and efficient solution to overcome common testing challenges. Playwright sharding empowers development teams to streamline their workflows, accelerate release cycles, and deliver high-quality web applications with confidence.