What are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a distinct class of AI models, boasting unparalleled capabilities across multiple modalities. Text, image, video – the boundaries blur under their computational prowess. But their magic lies deeper. They understand context, learn from mistakes, and even use tools like code or video transcriptions.
Their strengths stem from their colossal training datasets and billions of parameters (model weights) that can be adjusted during training and are fine-tuned to get the model proficient in specific tasks such as sentence completion and context-driven decision-making.
For Ultimate, this emerging technology allows for innovative ways of addressing user requests and providing solutions that operate contextually with minimal training needs, reducing the workload on human agents.
Recognising the transformative potential of LLMs, we actively integrated these models into our bots’ capabilities, enhancing our customer support automation platform. Our approach is twofold: embracing the innovative power of LLMs while remaining acutely aware of the challenges they present, such as the risk of generating inaccurate or ‘hallucinated’ information.
Ultimate’s success in managing these risks is deeply rooted in our early investment into traditional AI technologies such as Intent classification models and range of NLP models. This solid foundation helped us to craft an unique hybrid approach that merged established AI practices with novel functionalities of LLMs. This strategic blend not only minimized risks but also played a pivotal role in gradually fostering customer confidence in LLMs.
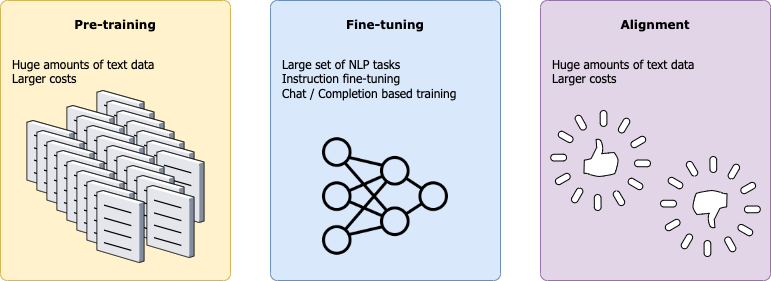
Training a LLM
The first step in a typical training pipeline involves training an extensive collection of samples, which undergo specific preprocessing steps for cleaning, giving the model its understanding of the world and its fundamental linguistic knowledge. This step is considered one of the most resource-intensive and both time and cost can be limiting factors here.
The fine-tuning phase focuses on training a language model for specific Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, such as sentiment analysis, question answering, translation, and more. Mastering these basic tasks is crucial for the LLM to be able to understand instructions and be competent enough to apply them. Essentially the model is specializing through practice.
Alignment is one of the most critical steps in the training pipeline and usually comes last. This phase is mostly concerned with aligning the model with human preferences. Addressing biases is particularly significant in this step to ensure these models resonate with our values and expectations.
The challenge of training models, taking into account their size and significant dependence on vast datasets, proves to be a major hurdle for many companies seeking to harness their capabilities. To address this, prominent tech companies, both large corporations and startups, have entered the scene, offering services for these models known as AI Service Providers, delivering AI as a Service (AIaaS). Notable entities in this domain include OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, recognized as major players in the field. Additionally, other companies and startups, such as Anthropic, are also offering similar services, each with distinct qualities and features.
In contrast, the open-source AI community is actively pursuing the democratization of Large Language Models (LLMs). The recent model releases from this community offer a glimpse of a promising future for the democratization of AI.
At Ultimate, our focus goes beyond just addressing specific issues with these tools. We aim to offer solutions in over 100 languages while maintaining ethical standards. Our solution is designed to handle user queries in both single and multiple languages, as well as across languages. A cross-lingual approach means processing information in a language different from the user’s native language. Our priority is to provide secure and ethical responses, ensuring accuracy and avoiding hallucinations while effectively resolving the user’s inquiry.
Responding to users with a tone of voice that matches the brand is equally crucial as providing accurate information. This task becomes more challenging when dealing with not just one language but over 100 languages. Maintaining language neutrality and upholding it as a core feature of our product demanded extensive research and development efforts, especially in the face of emerging technologies.
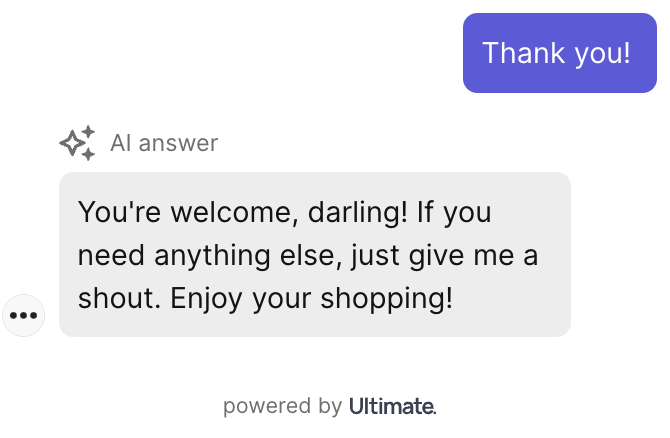
When working on the tone of voice, our bots would sometimes get a bit too sassy.
While research plays a vital role in our strategy, we have also developed a scalable solution to meet the needs of a large customer base. Delivering a high-quality, scalable solution remains paramount for our company.
LLMs: AI Upgrade for Smarter and Better Bots
Beyond sentence completion, large language models (LLMs) exhibit significant capabilities in information processing and knowledge application. Their proficiency in generating text sequences transcends simple context continuation, as they can leverage information from previous training stages to construct meaningful responses.
To illustrate, consider an LLM tasked with answering a question. It will not only access the immediate context but also draw upon its internal knowledge base, built during prior training across diverse datasets. This knowledge repository, encompassing factual information and world dynamics, enables the LLM to infer relationships and context-specific interpretations, leading tomore accurate and informative responses.
Furthermore, LLMs can extend their abilities beyond pure language to handle specific tasks, including mathematical computations. This demonstrates their capacity to develop rudimentary domain-specific knowledge and utilize it for targeted problem solving.
In essence, the core strengths of LLMs lie in their ability to comprehend and integrate information, access and apply internal knowledge, and reason within contextual boundaries. This combination allows them to adapt and handle a wide range of information types and tasks with increasing sophistication.
The appeal of large language models (LLMs) lies in their evolving capacity to handle user requests through increasingly innovative methods. This motivates Ultimate to continually explore novel solutions that leverage the latest advancements in LLM technology. For instance, the deployment of zero-shot bots, capable of learning within context and bypassing conventional training processes, presents a promising approach to automating customer support tasks. Additionally, uGPT, our flagship LLM product, showcases remarkable generalization capabilities by offering pre-trained solutions that require minimal further customization. This feature positions uGPT as a practical option for clients seeking to reduce reliance on human agents.
Misinformation in Generative AI: the Challenges with Hallucinations
Generative AI possesses the potential to propagate misinformation as a result of its learning process. While the primary objective is pattern recognition, there are instances where LLMs replicate the exact content they were trained on, presenting challenges related to the rights and regulations governing the training data. Hence why Ultimate would never share any customer data with external parties to improve LLMs.
- Copyrighted Material: Instances where GenAI reproduces copyrighted intellectual property, such as books or paintings.
- Privacy Concerns: Replicating personal information, such as emails, bank account numbers, IBANs, etc., from the training data.
Beyond these cases, where outputs are directly derived from training data, there is also the potential for fabricating false narratives and distorting reality, a phenomenon known as “hallucination”.
While the LLM’s acquired knowledge of the world is beneficial in dealing with various problems, it is a double edged sword as it may have acquired knowledge during training that is either very shallow, biased or simply false, making LLMs prone to hallucinate.
Addressing hallucinations was crucial in the development of UltimateGPT (uGPT), to ensure our bots give accurate answers.
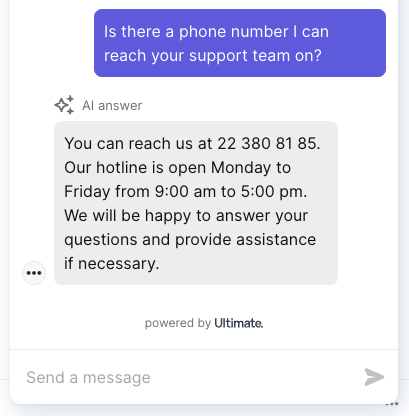
Early release of uGPT - this phone number was entirely made up.
To address this we focussed our research extensively on distinguishing between casual customer small talk and customer queries that need factual responses. We retrieve information from different sources like our customers’ knowledge bases and put strict guard rails in place to ensure accurate answers and to combat hallucinations when users ask for information.
Creating Factual Next Generation Customer Service Bots
At Ultimate we build uGPT as a RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) system to harness the power of LLMs responsibly.
We incorporated a robust in-house IR (Information Retrieval) system, that is designed to retrieve information from diverse sources, incorporating various parameter settings like locale in a cross-lingual manner. This approach allows our customers to effortlessly import data from different sources and languages, enabling them to address user inquiries effectively.
To ensure the efficiency of this system, we compared its capabilities and performance to traditional IR systems. Quantifying success in this specific context posed challenges, leading us to employ diverse techniques such as user simulation to measure its effectiveness. Our results revealed it is significantly more performant.
Beyond the IR system itself, we established a pipeline to enrich queries with additional context. This specific type of query expansion plays a pivotal role in enhancing response quality by generating answers not solely from a single source but from a combination of them.
Beyond Sentence Completion - the Evolution and Future of LLMs
LLMs are evolving quickly. From their humble beginnings as handy writing assistants with a focus on sentence completion, their capabilities have significantly expanded. They now exhibit a deep understanding of context and employ in-context learning to adapt to various tasks without requiring specific training.
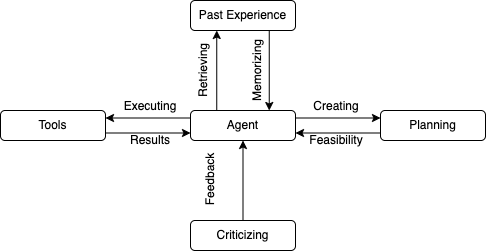
LLMs can utilize tools, plan their application and learn from environmental feedback, adjusting based on outcomes. Although a standalone LLM may not be optimal for certain data formats, like video, equipping them with tools such as video transcription allows them to understand and respond to video content effectively. Advanced functionalities, like code execution, empower LLMs not just to use existing tools but also to generate tools for themselves. The coding capabilities of these models allow them to create customized tools and troubleshoot issues when software does not function as expected.
LLMs can be utilized to create agents that can strategize and leverage past experiences to devise more efficient solutions within their operational parameters. Additionally, they can refine their performance by incorporating self-assessment and self-critique mechanisms.
Given these impressive capabilities, LLMs have become invaluable across a myriad of domains, ranging from coding to serving as everyday personal assistants.
One of our primary initiatives is developing the next generation of our uGPT product: zero-shot bots, aiming to get rid of intent training and expressions entirely. First tests have shown promising outcomes compared to traditional bots which still required explicit training. Within this context, we have explored the reasoning capacities of LLMs to enhance the explainability of our systems. Our objective extends beyond creating efficient but also transparent solutions; enabling our customers to understand and improve these models.
At the forefront of AI advancements, LLMs continue to redefine possibilities and present significant potential but also call for careful consideration regarding responsible deployment. As LLMs increasingly integrate into our daily routines, it’s essential to understand the technology, acknowledge its limitations, and prioritize ethical considerations.
A primary challenge in this domain is producing responses that are not only accurate and offer meaningful insights. Utilizing LLMs for automating customer service not only expedites problem-solving for users but also enables businesses to build enhanced solutions.
RAG systems, such as uGPT, embrace the transformative potential of LLMs, while prioritizing factual accuracy and avoiding unreliable outputs.
With advancements in capabilities such as tool utilization and self-enhancement, GenAI and LLMs emerge as pivotal tools in effectively addressing user queries that demand accurate information and actionable responses.